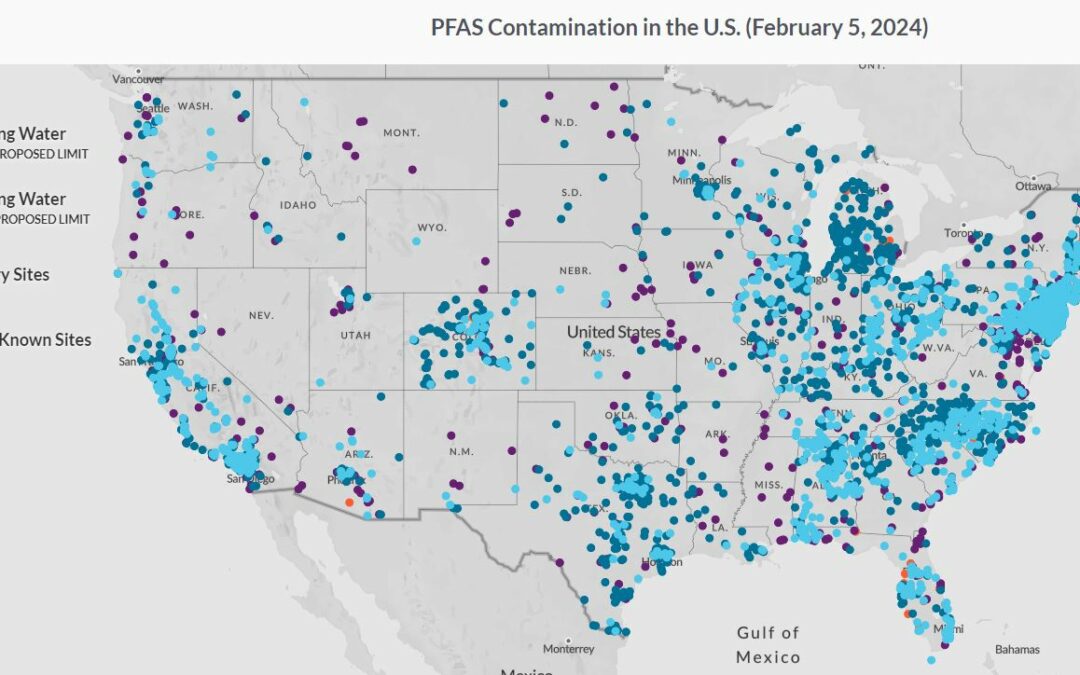
At Elder's Pure Water, we know that PFAS is a growing concern for Dallas, Fort Worth, and Westoplex families and we care about its impact on the health of our local community.
PFAS are a large family of man-made chemicals used in various ways since the 1940s. Most commonly found in consumer products like non-stick cookware, food packaging, stain-resistant fabrics, and firefighting foams. The most common and most studied forms of PFAS are PFOA and PFOS. In this article, we’ll discuss what PFAS is, where it comes from, why you should be concerned, and the best ways to protect yourself and your family from these chemicals.
According to the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIH) per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS chemicals) make up a vast, complex category of synthetic chemicals found commonly in consumer goods around the world. These chemicals are used for various reasons like keeping food from sticking to packaging and cookware, making clothes and carpets stain-resistant, and making firefighting foam more effective. PFAS chemicals are characterized by a chain of interconnected carbon and fluorine atoms, PFAS molecules possess an exceptionally robust carbon-fluorine bond. This contributes to their resistance against easy degradation in the environment.
The American Cancer Society provides these definitions:
- PFAS – lab-made chemicals known as perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances. PFAS is the category.
- PFOA – Perfluorooctanoic Acid (Compound)
- PFOS – Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (Compound)
Where Does PFAS Come From?
PFAS are commonly used in the aerospace, automotive, construction, and electronics industries. Over time, the inappropriate handling of PFAS has caused contaminated soil, water, and air. PFOA and PFOS are a manufactured perfluorochemical and a byproduct in producing fluoropolymers. Perfluorochemicals (PFCs) are a group of chemicals used to make fluoropolymer coatings and products that resist heat, oil, stains, grease, and water.
How Does PFAS Get Into Our Drinking Water?
Regrettably, manufacturers, even some who knew of their dangers, failed to dispose of these chemicals responsibly decades ago. This has led to them seeping into the groundwater supply across the nation and increased PFAS contamination and PFAS exposure for the entire population. These substances are called forever chemicals because they are nearly impossible to destroy. According to the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency), it can take decades or longer for some forms of PFAS to break down. Ongoing research focuses on remediation, raising critical questions about how to extract PFAS from the environment and water and ultimately how to eliminate them.
How are People Exposed to PFAS?
People are also exposed to PFAS contamination when they consume PFAS-contaminated water or food, use products made with PFAS like non-stick skillets, or breathe air containing PFAS. Because PFAS breaks down slowly if at all, people and animals are repeatedly exposed to them. The PFAS detected in blood levels can also build up over time.
Why Should You Be Concerned About PFAS in Your Drinking Water?
Although the levels in drinking water are usually low, they can be higher in certain areas, such as near industrial plants that have used these chemicals. Even at low levels, recent peer-reviewed scientific studies show a range of potential health risks associated with exposure to specific levels of PFAS. These harmful health effects include reproductive issues like decreased fertility and heightened high blood pressure in pregnant women. Developmental effects on children may result in low birth weight, accelerated puberty, bone variations, and behavioral changes. Other health effects include an increased risk of certain cancers, such as prostate, kidney, and testicular cancers, has also been identified.
PFAS exposure also has other associated health risks such as a reduced ability of the body’s immune system to fight infections, leading to compromised vaccine responses. Additionally, interference with the body’s natural hormones, along with elevated cholesterol levels and an increased risk of obesity, adds to the complex array of health concerns associated with these persistent chemicals.
The ATSDR website (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry) emphasizes that the studies it discusses do not uniformly involve identical groups of people, consistent types of exposure, or the same PFAS varieties. Given the status of PFAS as an emerging contaminant, there is a recognized need for additional research to fully understand the physical effects that come from exposure.
How Can You Guard Against PFAS in Your Water?
Two proven technologies have undergone testing and received recognition for their ability to eliminate up to 98% of PFAS from drinking water. Both the Water Quality Research Foundation (WQRF) and a study conducted by Purdue University have identified reverse osmosis and activated carbon as dependable solutions for effective PFAS removal.
A reverse osmosis system uses a membrane and additional filters to effectively reduce most PFAS from your water. This membrane, driven by pressure and having a small pore size, plays a crucial role in the purification process as it allows only a minimal number of contaminants to pass through. A reverse osmosis unit is typically installed as a point-of-use system at a specific faucet, such as the kitchen sink. The focus is on purifying water rather than just filtering it. It’s not typically intended for whole-home purification.
For comprehensive whole-home removal, activated carbon is another effective solution. Its effectiveness depends on the water’s exposure time to the proper level of carbon media. This process is not intended for DIY implementation. It’s important that a local water treatment professional installs this type of system to ensure the correct removal of PFAS contaminants.
A third technology currently under research involves an Ion Exchange Resin. Unlike the resin found in water softeners, this innovative resin is specifically designed for PFAS removal. Ongoing research holds promise for further advancements in this area.
What is the Next Step for You?
Given the complexity of the available information, you might be wondering about the best course of action. Conduct thorough research and gather as much information as possible. Whether your water comes from a municipal system or well water, reaching out to a local water treatment professional is essential.
At Elder's Pure Water, we have over 8 years of experience and an intimate knowledge of the local water supply and we understand the needs of the local Dallas, Fort Worth, and Westoplex communities. Our goal is to provide you with knowledge about your unique water supply and recommend appropriate treatment methods so that you can make the best decision possible for the health of your family. To learn more about your water and explore possible solutions for your family give us a call at 817-631-4967 or contact us here.